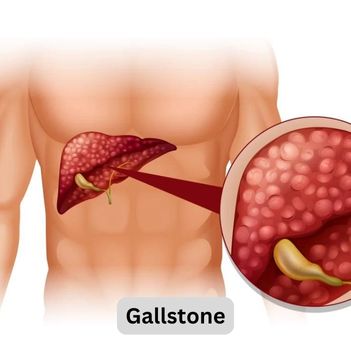
Introduction: Gallstones are a common medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide. These small, hard particles can form in the gallbladder, causing discomfort and potentially leading to more serious complications. In this blog, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for gallstones, providing valuable insights into this often overlooked health issue.
I. What are Gallstones?
Gallstones are solid particles that form in the gallbladder, a small organ located beneath the liver. The gallbladder plays a crucial role in the digestive process by storing bile, a digestive fluid produced by the liver. Gallstones can range in size from tiny grains to larger stones, and they can vary in composition, with cholesterol and bilirubin being the primary components.
II. Causes of Gallstones:
Several factors contribute to the formation of gallstones, and understanding these causes can help individuals make informed lifestyle choices to reduce their risk. Key factors include:
Excess Cholesterol: High levels of cholesterol in the bile can lead to the formation of cholesterol gallstones.
Bilirubin Imbalance: Conditions that cause an imbalance in bilirubin levels can contribute to the development of pigment gallstones.
Obesity: Being overweight or obese increases the risk of gallstones, as excess body weight can lead to higher cholesterol levels in the bile.
Rapid Weight Loss: Crash dieting or undergoing weight loss surgery can result in a sudden release of cholesterol, promoting gallstone formation.
Pregnancy: Hormonal changes during pregnancy can increase the risk of gallstones.
Genetics: A family history of gallstones may predispose an individual to this condition.
III. Symptoms of Gallstones:
Gallstones often go unnoticed until they cause complications. Common symptoms include:
Abdominal Pain: Sharp pain in the upper abdomen, especially after eating fatty foods.
Nausea and Vomiting: Gallstones can cause digestive disturbances, leading to nausea and vomiting.
Jaundice: In cases where gallstones block the bile ducts, yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice) may occur.
Fever and Chills: Inflammation or infection of the gallbladder can cause fever and chills.
IV. Diagnosis and Treatment:
If gallstones are suspected, medical professionals may use various diagnostic tools, such as ultrasound, CT scans, or blood tests, to confirm the diagnosis. Treatment options depend on the severity of symptoms and may include:
Watchful Waiting: Asymptomatic gallstones may not require immediate treatment but will be monitored for any changes.
Medications: Certain medications can dissolve gallstones, although this approach is less common.
Surgery: The most common treatment for symptomatic gallstones is the surgical removal of the gallbladder, known as cholecystectomy.
Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can help prevent gallstones.
Conclusion:
Gallstones are a prevalent health concern that can lead to significant discomfort and complications if left untreated. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to minimize their risk and maintain optimal gallbladder health. If experiencing symptoms or at risk, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and guidance on the most appropriate course of action.